
Soot in your nostrils or throat are an indicator of smoke inhalation and the extent of the smoke inhalation.Seizures and coma are also possible after smoke inhalation.Low oxygen levels and chemical asphyxiates can cause changes such as confusion, fainting, and decreased alertness.Smoke can irritate your eyes and cause redness.
#Too much carbon monoxide symptoms skin
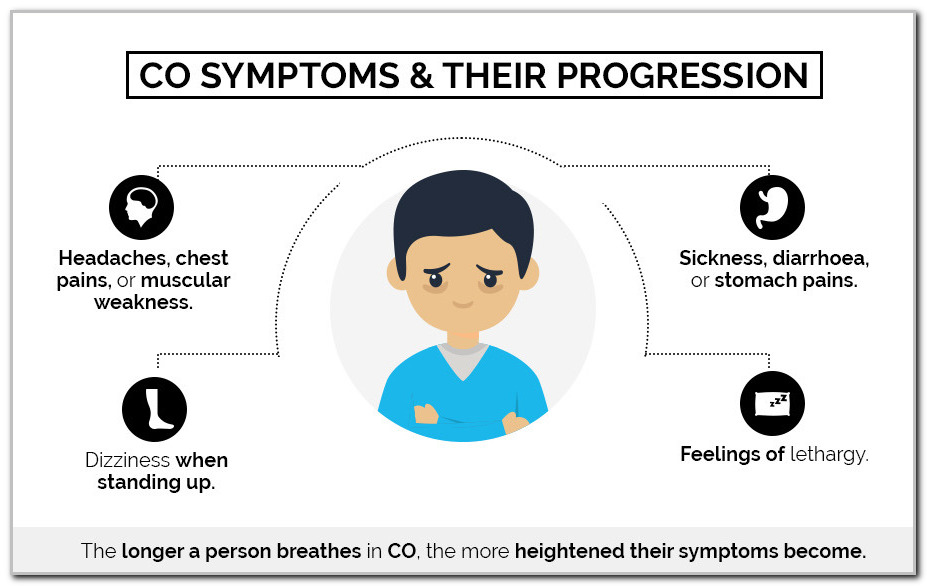
Skin can be pale and bluish due to lack of oxygen, or bright red due to carbon monoxide poisoning.Fluids may collect in the upper airway and result in a blockage.Chemicals may irritate and injure your vocal chords and cause swelling and tightening of the upper airways.Along with headache, carbon monoxide poisoning can also cause nausea and vomiting.Exposure to carbon monoxide, which occurs in every fire, can cause headache.Rapid breathing can result from an attempt to compensate for the damage done to the body.Smoke inhalation can interfere with your blood’s ability to carry oxygen.Injury to your respiratory tract decreases oxygen delivery to your blood.Mucus may be clear, gray, or black depending on the volume of burned particles in your trachea or lungs.Increased mucus production and the tightening of the muscles in your airway lead to reflex coughing.The mucous membranes in your respiratory tract secrete more mucus when they become irritated.Smoke inhalation can cause several signs and symptoms that can range in severity. Your risk for permanent damage from smoke inhalation is greater if you have any of these conditions. Inhalation injuries can worsen heart and lung conditions, such as: Carbon monoxide, which is the leading cause of death in smoke inhalation, is one of these compounds. Chemical asphyxiatesĬompounds produced in fires can cause cell damage in your body by interfering with the delivery or use of oxygen. Ammonia, sulfur dioxide, and chlorine are examples of chemical irritants in smoke. These chemicals can damage your respiratory tract, causing swelling and airway collapse. Irritant compoundsĬombustion can cause chemicals to form that injure your skin and mucous membranes. Smoke also contains products, such as carbon dioxide, that cause harm by further limiting the amount of oxygen in the air. Combustion uses up the oxygen near a fire, leaving you without oxygen to breathe. There are two ways that smoke can deprive you of oxygen. Burning materials, chemicals, and the gases created can cause smoke inhalation by simple asphyxiation (lack of oxygen), chemical irritation, chemical asphyxiation, or a combination of them.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
